Explore the First Humans on Earth and the oldest fossils – Retro Timeline
The Middle Awash region in Ethiopia is home to a remarkable discovery that has revolutionized our understanding of human evolution. Over 160,000 years ago, the first humans on earth, known as Herto Man, roamed the African savannah, leaving behind fossils that have provided valuable insights into their lives. These ancient ancestors have sparked heated debates among scientists about the origins of our species and their significance in human evolution.
The discovery of Herto Man in 1997 at the Middle Awash archaeological site was a watershed moment in the study of human evolution. Despite facing challenges such as scorching heat, flash floods, and armed bandits, a team of scientists uncovered the remains of three adults and one child. These fossils, dating back over 160,000 years, have been well-preserved, allowing for detailed study and analysis.
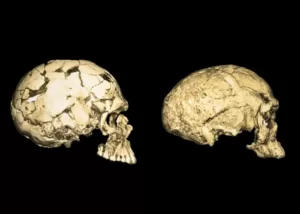
The age and research history of Herto Man shed light on their significance in human evolution. The initial discovery of three crania and other skeletal fragments provided early evidence of complex behaviors such as mortuary practices. Further analyses revealed a combination of archaic and modern traits in the Herto Man, suggesting they were anatomically modern humans. Various dating methods indicate that Herto Man lived between 160,000 to 154,000 years ago, making them the oldest known fossils of modern humans.
The physical characteristics of Herto Man, particularly their skulls, offer crucial insights into the evolutionary history of Homo sapiens. Their large cranial capacity, resembling that of modern humans, along with a high and rounded braincase and a vertical forehead, indicate similarities to us. However, distinctive features such as prominent brow ridges and a pronounced bulge at the back of the skull set them apart from modern humans, highlighting their unique traits.
The debate surrounding Herto Man centers on whether they are truly Homo sapiens or a missing link between early hominids and modern humans. Some researchers argue that Herto Man represents early members of Homo sapiens, while others suggest they may be a transitional form between Homo erectus and Homo sapiens. Detailed analyses of their cranial features and genetic makeup support the classification of Herto Man as anatomically modern humans.
Despite significant findings, many questions remain unanswered, paving the way for future research on Herto Man. Researchers aim to explore their cultural and behavioral characteristics, including diet, hunting practices, social structure, and tool use. The relationship between Herto Man and other early human species, as well as the climate and environment of the Middle Awash region during the Pleistocene epoch, are also areas of interest for further investigation.
In conclusion, the discovery of Herto Man has opened up exciting new avenues for research and has the potential to greatly enhance our understanding of human evolution. While uncertainties persist, ongoing research on these ancient humans will undoubtedly shed light on the mysteries surrounding our earliest ancestors.







